Long term power cycling will fatigue standard thermoelectric coolers by creating micro cracks in the semiconductor elements or solder joints which degrade the performance over.
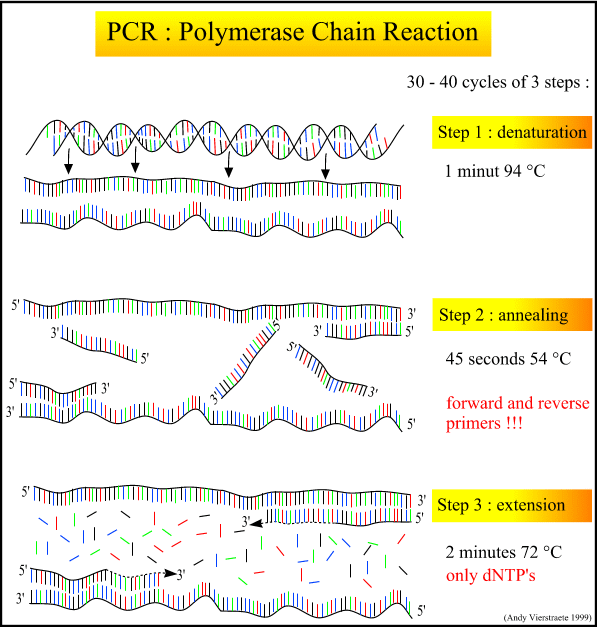
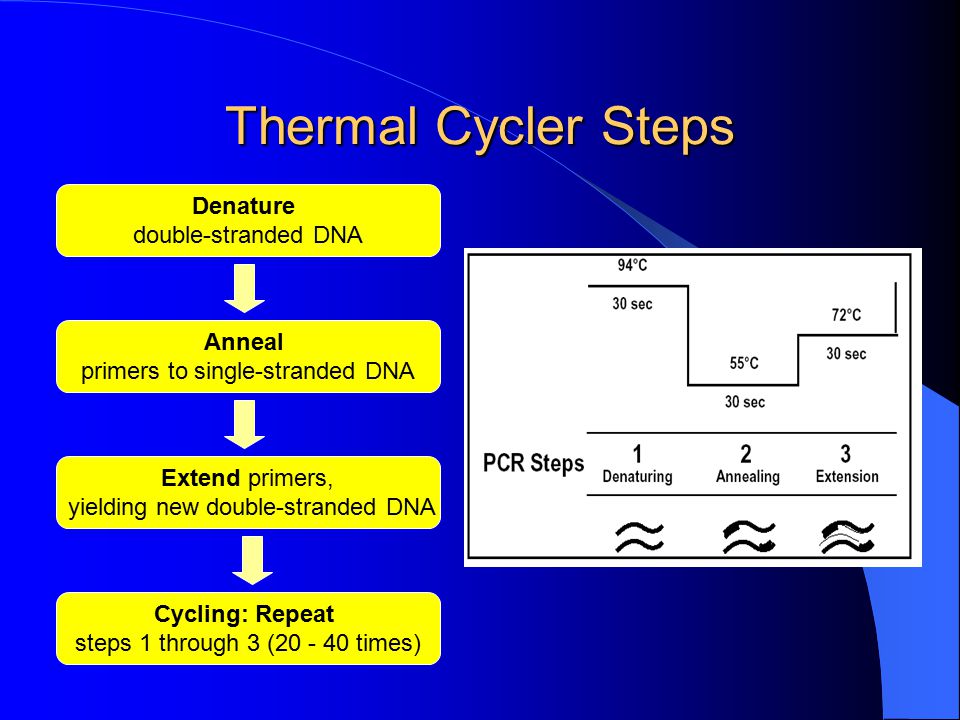
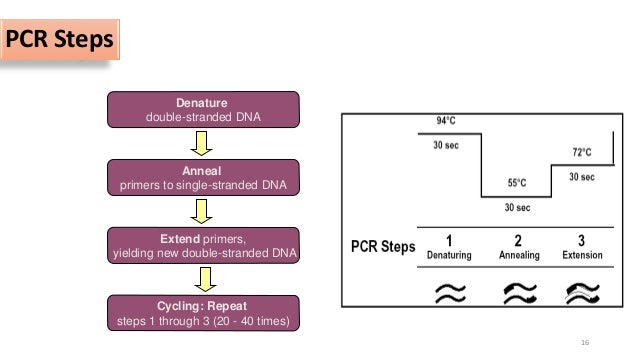
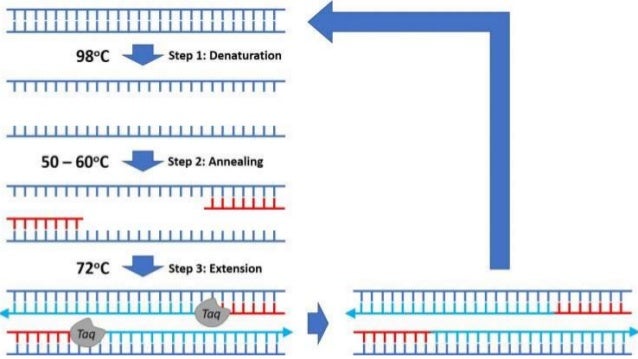
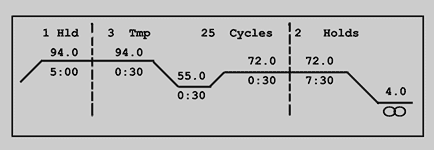
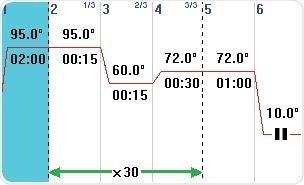
Pcr thermal cycler steps.
The thermal cycler also known as a thermocycler pcr machine or dna amplifier is a laboratory apparatus used to amplify segments of dna via the polymerase chain reaction pcr.
Several thermal cyclers however showed slow changes in temperature at the beginning of a pcr step resulting in curved temperature profiles which substantially shortened the duration of the temperature plateau i e more than 20 of the programmed duration.
Pcr was invented in 1984 by the american biochemist kary mullis at cetus corporation it is fundamental to much of genetic testing including analysis of.
Similarly well to well consistency of the temperature across a thermal block is critical to obtaining reliable and reproducible pcr results 2.
In this example taq polymerase is being added for a hot start type of pcr described later.
The small tubes contain the chemicals needed for a single pcr.
This tutorial will show you how to make a thermal cycler from scratch for about 85.
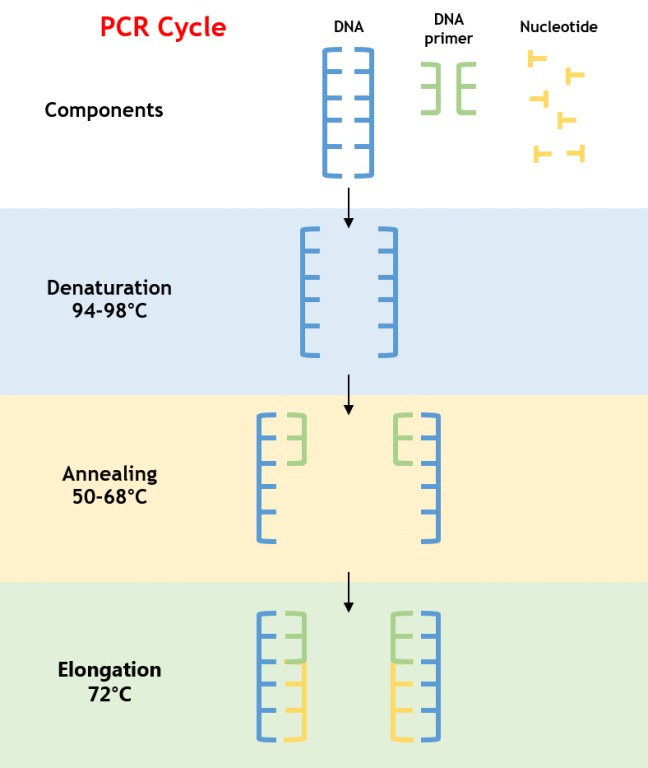
Pcr uses thermal cyclers to heat and cool a dna sample based on a predefined series of temperature steps to facilitate the amplification of dna and identify biomarkers.
Thermocyclers or thermal cyclers are instruments used to amplify dna and rna samples by the polymerase chain reaction.
The accuracy of a thermal cycler s temperature may determine the success or failure of pcr because of the temperature dependence of the three main steps of pcr 3.
The device has a thermal block with holes where tubes holding the pcr reaction mixtures can be inserted.
Thermal cyclers may also be used in laboratories to facilitate other temperature sensitive reactions including restriction enzyme digestion or rapid diagnostics.
The cycler then raises and lowers the temperature of the block.
The thermocycler raises and lowers the temperature of the samples in a holding block in discrete pre programmed steps allowing for denaturation and reannealing of samples with various reagents.
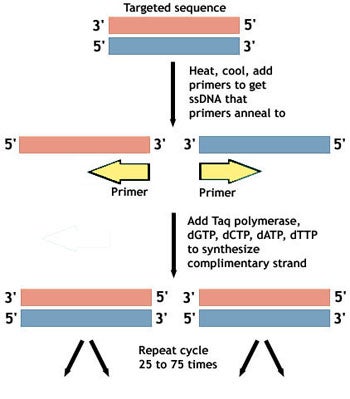
In short pcr polymerase chain reaction amplifies bits of dna creating millions of copies of a target sequence.
The polymerase chain reaction or pcr is a ubiquitous laboratory technique of molecular biology to amplify a target dna sequence to millions of copies since pcr technology relies on repeated thermal cycling for target amplification the equipment to automate the process thermal cyclers may play a critical role in the success of experiments this section covers the evolution and advancement.
You can use it to test a dna sample for a specific gene for instance to check for genetic modification in food and for hereditary gene testing.
Polymerase chain reaction pcr is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies of a specific dna sample allowing scientists to take a very small sample of dna and amplify it to a large enough amount to study in detail.